Description
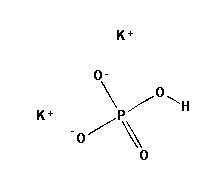
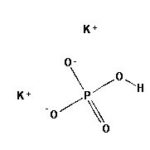
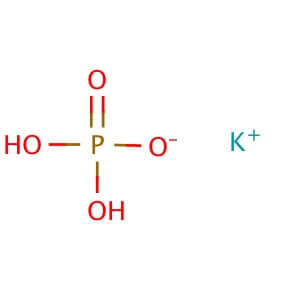
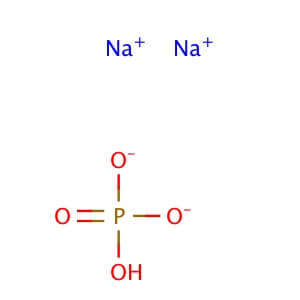
Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous (K2HPO4) is a reagent with a very high buffering capacity. Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous is widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry, and chromatography. Potassium phosphate occurs in several forms: monobasic (KH2PO4), dibasic (K2HPO4), and tribasic (K3PO4). Neutral potassium phosphate buffer solutions may be prepared with a mixture of the monobasic and dibasic forms to varying degrees, depending on the desired pH. Potassium Phosphate buffers are very useful in numerous applications, but with the following limitations: precipitation of Ca2+ and Mg2+, inhibition of restriction enzyme activity, and interference in DNA ligation or bacterial transformation protocols. Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous has been used to study the effects of freezing and thawing on the stability of proteins sensitive to conformational changes; it was found that Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous buffers offered improved pH stability as opposed to NaP buffers. Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous has also been used for the extraction of keratohyalin protein from bovine tissue. Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous is also known as Dipotassium hydrogenphosphate, Dipotassium phosphate, and sec.-Potassium phosphate. Additional forms available: Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous Potassium Phosphate, Monobasic Potassium phosphate tribasic Potassium phosphate tribasic monohydrate Potassium phosphate dibasic solution Potassium Phosphate Monobasic solution


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.