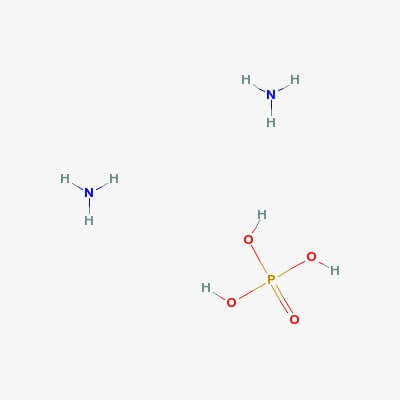
Ammonium Phosphate Dibasic
CAS NO: 7783-28-0
Molecular Formula: HPO4·(NH4)2
Molecular Weight: 132.06
Description Replaces AX1355-1; AX1355 Synonyms Ammonium biphosphate, Ammonium phosphate dibasic, Diammonium hydrogen phosphate, Fyrex Description di-Ammonium hydrogen phosphate Product Information CAS number 7783-28-0 EC number 231-987-8 Grade ACS,Reag. Ph Eur Hill Formula H₉N₂O₄P Chemical formula (NH₄)₂HPO₄ Molar Mass 132.06 g/mol HS Code 3105 30 00 Quality Level MQ300 Physicochemical Information Density 1.620 g/cm3 Melting Point 155 °C (decomposition) pH value 7.5 – 9.0 (132.1 g/l, H₂O, 25 °C) Vapor pressure 0.076 Pa (20 °C) Bulk density 800 – 1000 kg/m3 Solubility 690 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 6500 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rabbit > 7950 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips (Item No. 109535). Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Transport Information Declaration (railroad and road) ADR, RID Kein Gefahrgut Declaration (transport by air) IATA-DGR No Dangerous Good Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG-Code No Dangerous Good Specifications Assay (acidimetric) ≥ 99.0 % Insoluble matter ≤ 0.005 % pH-value (5 %; water; 25 °C) 7.8 – 8.1 pH-value (20 %; water) about 8 Chloride (Cl) ≤ 0.0005 % Nitrate (NO₃) ≤ 0.001 % Sulfate ≤ 0.004 % Heavy metals (as Pb) ≤ 0.0005 % Ca (Calcium) ≤ 0.001 % Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.001 % K (Potassium) ≤ 0.001 % Mg (Magnesium) ≤ 0.0005 % Na (Sodium) ≤ 0.001 % Corresponds to ACS, Reag. Ph Eur Calcium Chloride Dihydrate
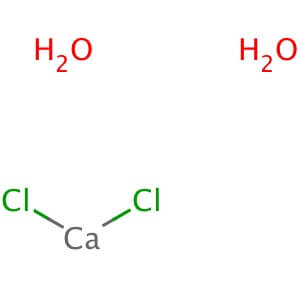
CAS NO: 10035-04-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- CaCl2.2H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 147.01 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description A White, Crystalline powder or fragments or granules, odorless, hygroscopic. White or almost white, crystalline powder, hygroscopic. White or almost white, crystalline powder, hygroscopic. Solubility – Freely soluble in water and soluble in ethanol (96 %) – Appearance of solution Clear and not more intensely colored than reference solution YS6. 10 % solution is clear and not more intensely colored than reference solution Y6. – Identification (A) Reaction Of Calcium
(B) Reaction of Chlorides
(C) Assay
A. Reactions of Calcium salts B. Reactions of Chlorides
A. 10% solution gives reaction of chloride B. It gives reaction of calcium
C. It complies with the limit test of assay
A. Reactions of Calcium salts B. Reactions of Chlorides
Acidity or Alkalinity To 10 ml of freshly prepared 10 % w/v solution add 2 drops off phenolphthalein solution. Titrate with 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide. If the solution is red , than not more 0.2 ml of 0.01 M HCL need to discharge the color and if the solution is colorless, not more than 0.2 ml NaOH is required to turn it red. – pH – – 4.5 – 9.2 Arsenic NMT 3 ppm. – – Barium After not less than 15 min. the solution is not more opalescent than a mixture of 10 ml of solution and 1 ml of distilled water. After 15 min, Any opalescent in the solution is not more intense than that in a mixture of 1 ml of distilled water and 1.0 gm of sample. – Aluminum &Phosphate (IP)
No turbidity or precipitate is produced. No turbidity or precipitate is formed. NMT 1 ppm Iron , Aluminum &Phosphate – – No turbidity or precipitate is formed. Heavy metals NMT10 ppm – NMT10 ppm Iron NMT 20 ppm. NMT 10 ppm – Magnesium and Alkali salts NMT 1.0 % NMT 0.5 % NMT 1.0 % Sulphate NMT 300 ppm NMT 300 ppm – Organic Volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements Assay 97.0 % to 103.0 % 97.0 % – 103.0 % 99.0% – 107.0% Calcium Phosphate Di Basic
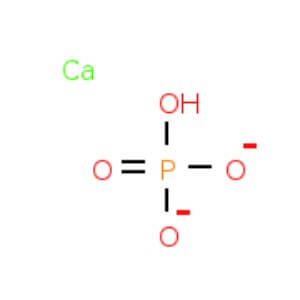
CAS NO: 7757-93-9
Molecular Formula: CaHPO4
Molecular Weight: 136.06
Description Synonyms Calcium orthophosphate, Calcium phosphate dibasic Description Calcium hydrogen phosphate Product Information CAS number 7757-93-9 EC number 231-826-1 Grade Ph Eur,BP,USP,FCC,E 341 (ii) Hill Formula CaHO₄P Chemical formula CaHPO₄ Molar Mass 136.06 g/mol HS Code 2835 25 00 Quality Level MQ500 Physicochemical Information Density 2.89 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 370 °C (decomposition) pH value 7 (10 g/l, H₂O, 20 °C) suspension Bulk density 900 kg/m3 Solubility 0.1 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 10000 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rabbit > 7940 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS TB8528000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Transport Information Declaration (railroad and road) ADR, RID Kein Gefahrgut Declaration (transport by air) IATA- DGR No Dangerous Good Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG- Code No Dangerous Good Specifications Identity passes test Assay (complexometric) 97.5 – 102.5 % Assay (complexometric; calculated on dried substance) 98.0 – 102.0 % Substances insoluble in hydrochloric acid ≤ 0.2 % Carbonate (as CO₂) passes test Chloride (Cl) ≤ 0.03 % Fluoride (F) ≤ 0.0050 % Sulfate (SO₄) ≤ 0.5 % Al (Aluminium) ≤ 0.0200 % As (Arsenic) ≤ 0.0001 % Ba (Barium) passes test Cd (Cadmium)* ≤ 0.0001 Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.0400 % Hg (Mercury) ≤ 0.0001 % Ni (Nickel)* ≤ 0.0010 Pb (Lead)* ≤ 0.0001 Sr (Strontium) ≤ 0.03 % V (Vanadium)* ≤ 0.0010 % Residual solvents (ICH Q3C) excluded by production process Loss on ignition (800 °C) 7.0 – 8.5 % Loss on drying ≤ 2.0 % Particle size (< 63 µm) about 99 % Elemental impurity specifications have been set considering ICH Q3D (Guideline for Elemental Impurities). Class 1-3 elements are not likely to be present above the ICH Q3D option 1 limit, unless specified and indicated (*). Corresponds to Ph.Eur.,BP,USP,FCC,E341 (ii) Conforms to the purity criteria on food additives, except for use as additive in infant and young child nutrition, according to the current European Commission Regulation. Disodium Edetate
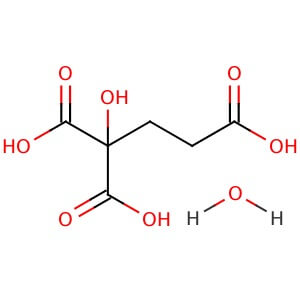
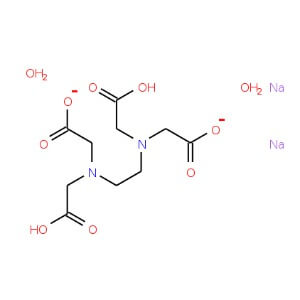
CAS NO: 6381-92-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- C10H14N2Na2O82H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 372.24 g/ mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description A white ,crystalline powder, Odourless White or almost white, crystalline powder. White or almost white, crystalline powder. Solubility – Soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 %) – Identification A. IR
B. Reaction
C. Reaction
D. Reaction
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. No precipitate is produced.
C. No precipitate is produced.
D. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. No precipitate is produced.
C. No precipitate is produced.
D. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. The red color is discharge, leaving a yellowish solution
C. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
Appearance of solution 5 % w/v solution in carbon dioxide free water is Clear & colorless Clear & colorless – pH 4.0-5.5 ( 5 % w/v solution ) 4.0-5.5 ( 5 % w/v solution ) 4.0-6.0 Loss on Drying – – 8.7 %-11.4 % Calcium – – No precipitate is formed. Impurity A Limit of nitrilotriacetic acid(USP)
NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % Heavy metals NMT 20 ppm – NMT 50 ppm Iron NMT 80 ppm NMT 80 ppm – Assay 98.5 %-101.0 % 98.5 %-101.0 % 99.0 %-101.0 %(on Dried basis) Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate
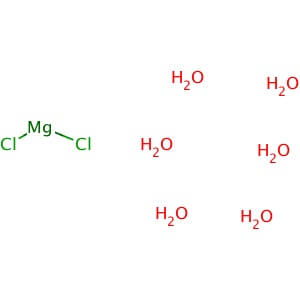
CAS NO: 7791-18-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA: MgCl2•6H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 203.30
Application: Magnesium Chloride, Hexahydrate is a source of magnesium ion and a co-foactor for many enzymes Purity: >99% Molecular Weight: 203.3 Molecular Formula: MgCl2•6H2O Description: Magnesium Chloride, Hexahydrate is widely used as a source of magnesium ion in chemistry and molecular biology applications. In biological systems, magnesium is a co-factor for many enzymes including deoxyribonuclease (DNase) and various restriction enzymes. Also plays a role in cell membrane integrity, muscle cell physiology, cardiovascular and muscular activity, and nucleic acid structure. Magnesium chloride solution is a favorable choice as an elution buffer for antibody affinity column purifications; it is much milder on most antigens than acid elution, allowing reuse of the antigen column. Also an essential cofactor for the DNA polymerase in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (20 mg/ml), and alcohol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 116-118° C (dec.) Density : 1.57 g/cm3 at 20° C Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate
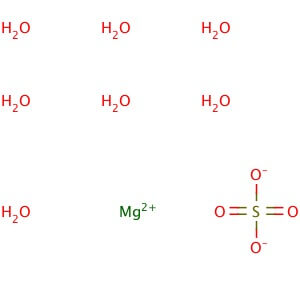
CAS NO: 10034-99-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- MgSO4.7H20
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 246.50 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Colorless crystals or white, Crystalline powder. White or almost white, crystalline powder or brilliant , colorless crystals. Colorless crystals or white, Crystalline powder Solubility – Freely Soluble in water , very soluble in boiling water and practically insoluble in ethanol (96 % )
Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
A : Reactions of Sulphates B : Reactions of Magnesium salts
A: It gives reaction of Sulphates. B :It gives reaction of magnesium
A: It gives reaction of Sulphates. B : It gives reaction of magnesium
pH of a 5% solution at 250C – – 5.0 – 9.2 Appearance of solution Dissolve 5 g in sufficient carbon dioxide free water to produced 50 ml (Solution A) is clear and colorless. Dissolve 5 g in sufficient carbon dioxide free water to produced 50 ml (Solution S) is clear and colorless. – Acidity or alkalinity NMT 0.2 ml of either 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of solution. NMT.0.2 ml of 0.01 M hydrochloric or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of indicator. – Arsenic NMT 2 ppm.
NMT 2 ppm – Heavy metals NMT 10 ppm.
– NMT 10 ppm Selenium – NMT 30 ppm Iron NMT 200 ppm. NMT 20 ppm NMT 20 ppm Chloride NMT. 300 ppm NMT. 300 ppm
NMT. 140 ppm Organic Volatile impurities – Meets the requirement Residual Solvents – Meets the requirement Loss on drying 48.0 to 52.0 %
48.0 % – 52.0 % NMT 2.0 % Loss on Ignition – – 40.0%-52.0% Assay (on dried basis) 99.0 % to 100.5 % 99.0 % – 100.5 % 99.0%- 100.5% Potassium Chloride
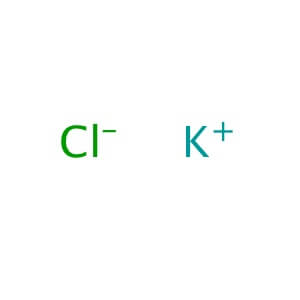
CAS NO: 7447-40-7
MOLECULAR FORMULA: KCl
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 74.55
Alternate Names: Potassium Chloride is also known as KCl. Application: Potassium Chloride is a common laboratory reagent and calibration standard for measuring electrical conducivity. Purity: >99% Description: Potassium Chloride is commonly used as a laboratory reagent as a standard. Potassium Chloride may be used as a calibration standard ionic solution for measuring electrical conductivity because Potassium Chloride solutions, when prepared carefully, produce repeatable measurable properties. Potassium Chloride is also a good source of ionic chloride, which should precipitate insoluble chloride salts upon addition to a solution of an appropriate metal ion. Oral Potassium Chloride is commonly used to replenish vital potassium in the body, and has also been shown to lower blood pressure. Potassium Chloride is commonly used in fertilizer. Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (340 mg/ml at 20° C), alcohol (slightly), and ethanol (1 g/250 mL). Insoluble in ether, and acetone. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 770° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 1500° C (lit.) Density : 1.98 g/cm3 at 25° C (lit.) Refractive Index : n20D 1.49 Ki Data : CA IV: Ki= 90 µM (human); CA I: Ki= 6 mM (human); CA IX: Ki= 33 mM (human); CA V: Ki= 156 mM (human); CA II: Ki>200 mM (human) Potassium Nitrate
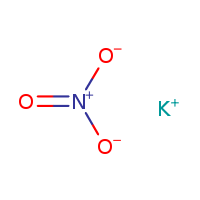
CAS NO: 7757-79-1
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- KNO3
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 101.1g/mol
SPECIFICATION BP USP Description White or almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals. White or almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals. Solubility Freely soluble in water, very soluble in boiling water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 %) – Identification A. Reaction
B. Reaction
A. It gives reaction of nitrates. B. It gives reaction of Potassium
A. It gives reaction of nitrates. B. It gives reaction of Potassium
Acidity or Alkalinity NMT 0.5 ml of 0.01 M HCl or 0.01 M NaOH is required to change the color of the indicator. – Reducible Substances The solution does not become blue within 2 min. – Chlorides NMT 20 ppm NMT 300 ppm Sulfates NMT 150 ppm NMT 1000 ppm Limit of Nitrite – NMT 5 ppm Heavy metals – NMT 20 ppm Arsenic – NMT 3 ppm Lead – NMT 10 ppm Ammonium NMT 100 ppm – Calcium NMT 100 ppm – Iron NMT 20 ppm NMT 10 ppm Residual Solvents – Meets the requirements. Sodium NMT 1000 ppm NMT 1000 ppm Loss on Drying NMT 0.5 % – Assay 99.0 %-101.1 % (on dried basis) 99.0 %-100.5 % Sodium Bi Carbonate
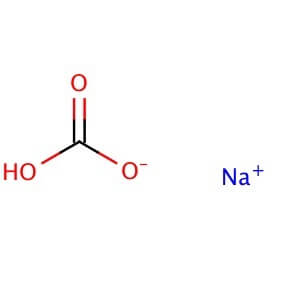
CAS NO: 144-58-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA: NaHCO3
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 84.01
Alternate Names: Sodium hydrogen carbonate Application: Sodium bicarbonate is a commonly used laboratory pH neutralizer that reacts with acids and bases Purity: ≥99% Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (50 mg/ml). Insoluble in ethanol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 300° C Density : 2.16 g/cm3 at 20° C Refractive Index : n20D 1.50 Ki Data : CA IV: Ki= 6.6 mM (human); CA I: Ki= 12 mM (human); CA IX: Ki= 13 mM (human); Astrosclerin-3: Ki= 22.8 mM (human); CA II: Ki= 85 mM (human) pK Values : pKa: 6.37, 10.25 in carbonic acid(25°C) Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous
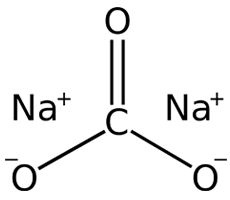
CAS NO: 497-19-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA : CNa2O3
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 105.99
Description Synonyms anhydrous soda Product Information Hill Formula CNa₂O₃ Chemical formula Na₂CO₃ Molar Mass 105.99 g/mol HS Code 2836 20 00 Quality Level MQ100 Applications Application Sodium carbonate anhydrous 99.999 Suprapur®. CAS No. 497-19-8, Physicochemical Information Boiling point 1600 °C (decomposition) Density 2.52 – 2.53 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 851 °C pH value 11.16 (4 g/l, H₂O, 25 °C) Bulk density 1100 kg/m3 Solubility 212.5 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 4090 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS Hazard Pictogram(s) Hazard Statement(s) H319: Causes serious eye irritation. Precautionary Statement(s) P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P280: Wear eye protection/ face protection. P305 + P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P337 + P313: If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/ attention. Signal Word Warning RTECS VZ4050000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips (Item No. 109535). Safety Information Categories of danger irritant Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Specifications Purity (metallic) ≥ 99.999 % Assay (acidimetric) ≥ 99.5 % Chloride (Cl) ≤ 10 ppm Phosphate (PO₄) ≤ 0.05 ppm Silicate (SiO₂) ≤ 5 ppm Sulfate (SO₄) ≤ 10 ppm Al (Aluminium) ≤ 0.05 ppm As (Arsenic) ≤ 0.1 ppm Ba (Barium) ≤ 5.0 ppm Ca (Calcium) ≤ 0.10 ppm Cd (Cadmium) ≤ 0.005 ppm Ce (Cerium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Co (Cobalt) ≤ 0.005 ppm Cr (Chromium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Cu (Copper) ≤ 0.005 ppm Eu (Europium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.05 ppm Hg (Mercury) ≤ 0.05 ppm K (Potassium) ≤ 1.0 ppm La (Lanthanum) ≤ 0.010 ppm Li (Lithium) ≤ 0.5 ppm Mg (Magnesium) ≤ 0.10 ppm Mn (Manganese) ≤ 0.010 ppm Ni (Nickel) ≤ 0.020 ppm Pb (Lead) ≤ 0.010 ppm Sc (Scandium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Sm (Samarium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Sr (Strontium) ≤ 0.10 ppm Tl (Thallium) ≤ 0.01 ppm Y (Yttrium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Yb (Ytterbium) ≤ 0.010 ppm Zn (Zinc) ≤ 0.010 ppm Urea
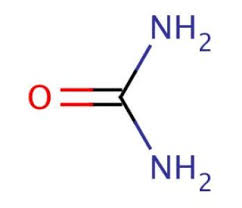
CAS NO: 57-13-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA: CH4N2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 60.06
Description Synonyms Carbamide, Carbonyl diamide, Diaminomethanone, Carbonyldiamine Product Information CAS number 57-13-6 Grade ACS,Reag. Ph Eur Hill Formula CH₄N₂O Chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂ Molar Mass 60.05 g/mol HS Code 3105 10 00 Structure formula Image Quality Level MQ200 Physicochemical Information Density 1.32 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 134 °C pH value 7.5 – 9.5 (480 g/l, H₂O, 25 °C) Vapor pressure <0.1 hPa (25 °C) Bulk density 720 – 760 kg/m3 Solubility 1000 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 8471 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rat 8200 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS YR6250000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 3 Relatively unreactive organic reagents should be collected in container A. If halogenated, they should be collected in container B. For solid residues use container C. Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +15°C to +25°C. Specifications Assay (ex N) 99.0 – 100.5 % Assay (ex N, calc. on dried substance) 99.0 – 101.5 % Purity (DSC (differential scanning calorimetry)) ≥ 99.5 mol% Identity (IR-spectrum) passes test Appearance of solution (10 %; Wasser; color) colourless Appearance of solution (10 %; Wasser; clarity) clear In water insoluble matter ≤ 0.003 % Acidity, Alkalinity ≤ 0.0005 meq/g Melting point (DSC) 132 – 135 °C NH₄ (Ammonium) ≤ 0.0500 % Chloride (Cl) ≤ 0.0005 % Sulfate (SO₄) ≤ 0.001 % Heavy metals (as Pb) ≤ 0.0004 % Biuret ≤ 0.05 % Sulfated ash (600 °C) ≤ 0.005 % Cu (Copper) ≤ 0.0001 % Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.0001 % Pb (Lead) ≤ 0.0002 % Loss on Drying (105 °C) ≤ 1.0 % Corresponds to ACS, Reag. Ph Eur
Showing all 12 items