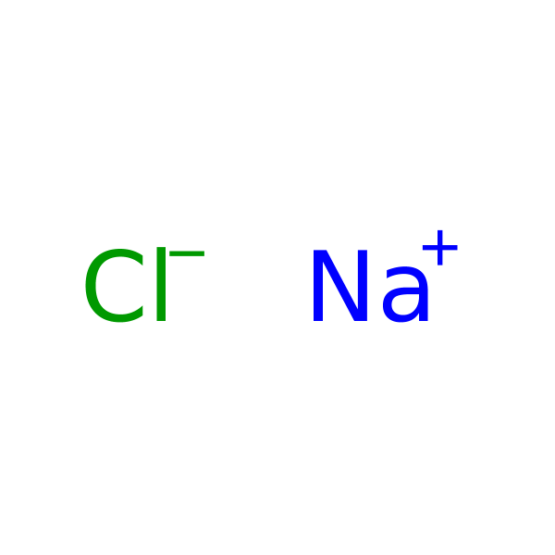
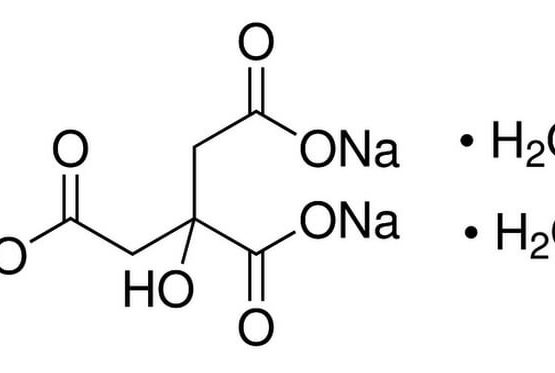
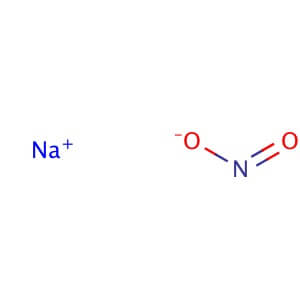
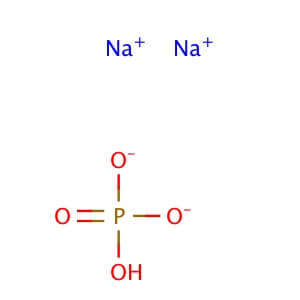
Sodium Chloride
CAS NO: 7647-14-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA: NaCl
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 58.44
Molecular Formula: NaCl Molecular Weight: 58.44 Alternate Names: Sodium Chloride is also known as table salt. Application: Sodium Chloride is used in biochemistry and molecular biology applications as a component of PBS and SSC buffers. Purity:≥98% Usage : If intended for use in cell culture applications, sterilization of the solution may be necessary. Pre-diluted buffer can be dispensed into aliquots and sterilized by autoclaving. Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (358 mg/ml at 20° C), alcohol (very slightly), glycerol (100 mg/ml), and ammonia. Insoluble in hydrochloric acid. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 801° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 1413° C Density : 2.17 g/cm3 at 20° C Refractive Index : n20D 1.54 Ki Data : Astrosclerin-3: Ki= 460 µM (Astrosclera willeyana); CA I: Ki= 6 mM (human); CA II: Ki= 200 mM (human) Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate
CAS NO: 6132-04-3
Molecular Formula: C6H5O7•2H2O•3Na
Molecular Weight: 294.1Alternate Names: Citric acid trisodium salt dihydrate; Trisodium citrate dihydrate Application: Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate (Molecular Biology Grade) is for the preparation of total ribosomal RNA from E. coli CAS Number 6132-04-3 Purity: ≥99.5% Molecular Weight: 294.1 Molecular Formula: C6H5O7•2H2O•3Na Description Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate (Molecular Biology Grade) is a source of Citric acid, a key metabolic intermediate. Citrate is the starting point of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Its concentration also coordinates several other metabolic pathways. Citric acid can form complexes with various cations, particularly with iron and calcium. In animals, citric acid improves the utilization of nutritional calcium. Usage : Preparation Instructions: One gram of sodium citrate dissolves in 1.3 ml of water at 25 °C and in 0.6 ml of boiling water. Poorly soluble in alcohol. pH: 7.5 – 9.0 (0.1 M in H2O, 25°C) Storage/Stability: Citrate buffers (pH 3-5) exhibit excellent stability at room temperature. Dilute solutions of citric acid (non-sterile) may ferment if left at room temperature. Non-sterile solutions should be stable for months stored at 2-8 °C. Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (29.4 g/L at 20 °C). Insoluble in alcohol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : >300° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 309.6° C at 760 mmHg Density : 1.86 g/cm3 Refractive Index : n20D ~1.58 (Predicted) pK Values : pKa: pK1: 3.14, pK2: 4.76, pK3: 6.40 Sodium Nitrite
CAS NO : 7632-00-0
Molecular Formula: NaNO2
Molecular Weight: 69.00
Application: Sodium nitrite is a strong oxidizer but stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage Purity: ≥97% Supplemental Information: This is classified as a Dangerous Good for transport and may be subject to additional shipping charges. Description Sodium Nitrite is soluble in water and readily forms colorless hexagonal crystals. It is a strong oxidizer but stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. Technical Information Appearance : Crystalline or powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (820 mg/ml at 20° C), methanol (4.5 mg/ml), ethanol (3 mg/ml), ether (slightly), and NH3 (very soluble). Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 271° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 320° C Density : 2.17 g/cm3 at 20° C IC50 : HL-60: IC50 = 94 µM (human) Ki Data : Salmonella Typhimurium carbonic anhydrase : Ki= 320 µM Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Anhydrous
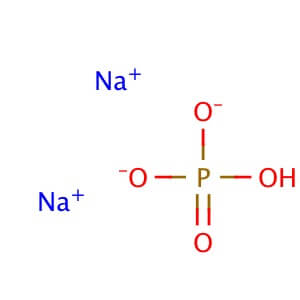
CAS NO : 7558-79-4
Molecular Formula:Na2HPO4
Molecular Weight: 141.96 g/mol
CAS No: 7558-79-4 MOLECULAR FORMULA: Na2HPO4 MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 141.98 Alternate Names: Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is also known as Disodium phosphate. Application: Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is reagent with high buffering capacity for molecular biology, biochemistry, and chromatography. Purity: ≥99% Description Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is a reagent with very high buffering capacity. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is especially useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic in the preparation of biological buffers. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic can be used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Additional forms available: Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic solution Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (118 mg/ml at 25° C). Insoluble in ethanol, alcohol, methanol, and n-octanol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 240.00° C Density : 1.52 g/cm3 Ki Data : CA IV: Ki= 9.8 µM (human) pK Values : pKa: pK1: 2.15 in phosphoric acid (25 C), pK2: 6.82 in phosphoric acid (25 C), pK3: 12.38 in phosphoric acid (25 C) Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dihydrate
CAS NO: 10028-24-7
Molecular Formula: Na2HPO4•2H2O
Molecular Weight: 177.99
Alternate Names: Disodium phosphate dihydrate;Disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate is a reagent with high buffering capacity Purity: ≥98% Description Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline and crystalline granules Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate
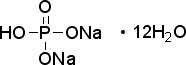
CAS NO: 10039-32-4
Molecular Formula: HPO4•2Na•12H2O
Molecular Weight: 358.14
Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate is a reagent with high buffering capacity CAS Number: 10039-32-4 Purity: ≥98% Molecular Weight: 358.14 Molecular Formula: HPO4•2Na•12H2O Supplemental Information: This is classified as a Dangerous Good for transport and may be subject to additional shipping charges. Description Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic (sc-202342, sc-215883 or sc-251042) in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Heptahydrate
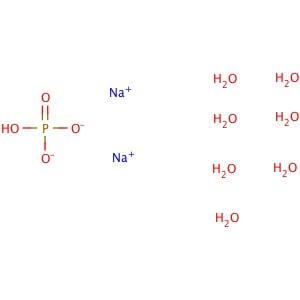
CAS NO: 7782-85-6
Molecular Formula:Na2HPO4•7H2O
Molecular Weight: 268.07
Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate is A high buffering capacity reagent CAS Number :7782-85-6 Purity: ≥98% Molecular Weight: 268.07 Molecular Formula: Na2HPO4•7H2O Descripton Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic (sc-202342, sc-215883 or sc-251042) in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (100 mg/ml). Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 48° C Density : 1.68 g/cm3 at 25° C (lit.) Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Dihydrate
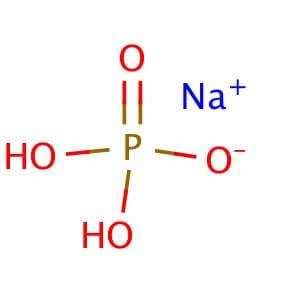
CAS NO : 13472-35-0
MOLECULAR FORMULA :NaH2PO4•2H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :156.01
Alternate Names: Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate; Monosodium phosphate dihydrate Application: Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate is a high buffering capacity reagent Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature Sodium Sulphate Anhydrous
CAS No:7757-82-6
Molecular Formula: Na2SO4
Molecular Weight: 142.04
Alternate Names: Disodium sulfate; Disodium sulphate; Bisodium sulfate
Application: Sodium sulfate anhydrous is for use as an inert drying agent
Purity: ≥99%
Product Information CAS number 7757-82-6 Hill Formula Na₂O₄S Chemical formula Na₂SO₄ Molar Mass 142.04 g/mol HS Code 2833 11 00 Quality Level MQ200 Applications Application Sodium sulfate anhydrous for synthesis. CAS No. 7757-82-6, EC Number 231-820-9. Physicochemical Information Density 2.70 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 888 °C pH value 5.2 – 8.0 (50 g/l, H₂O, 20 °C) Bulk density 1400 – 1600 kg/m3 Solubility 200 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat > 2000 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS WE1650000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips (Item No. 109535). Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Transport Information Declaration (railroad and road) ADR, RID Kein Gefahrgut Declaration (transport by air) IATA-DGR No Dangerous Good Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG-Code No Dangerous Good Product Information CAS number 7757-82-6 Hill Formula Na₂O₄S Chemical formula Na₂SO₄ Molar Mass 142.04 g/mol HS Code 2833 11 00 Quality Level MQ200 Applications Application Sodium sulfate anhydrous for synthesis. CAS No. 7757-82-6, EC Number 231-820-9. Physicochemical Information Density 2.70 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 888 °C pH value 5.2 – 8.0 (50 g/l, H₂O, 20 °C) Bulk density 1400 – 1600 kg/m3 Solubility 200 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat > 2000 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS WE1650000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips (Item No. 109535). Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Transport Information Declaration (railroad and road) ADR, RID Kein Gefahrgut Declaration (transport by air) IATA-DGR No Dangerous Good Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG-Code No Dangerous Good Sorbic Acid
CAS NO: 110-44-1
Molecular Formula: C6H8O2
Molecular Weight: 112.13
Alternate Names: α-trans-γ-trans-Sorbic acid; (E,E)-1,3-Pentadiene-1-carboxylic acid; 2,4-Hexadienoic acid Purity: ≥99% Technical Information Appearance : Crystalline Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water. Storage : Store at 4° C Melting Point : 135-137° C Density : 1.204 g/cm3 Synonyms 2,4-Hexadienic acid CAS number 110-44-1 Grade Ph Eur,BP,NF,FCC,E 200 Hill Formula C₆H₈O₂ Molar Mass 112.13 g/mol HS Code 2916 19 95 Quality Level MQ500 Boiling point 160 – 260 °C (1013 hPa) (decomposition) Density 1.2 g/cm3 (20 °C) Flash point 127 °C Ignition temperature >130 °C Melting Point 135 – 137 °C pH value 3.3 (1.6 g/l, H₂O, 20 °C) Vapor pressure 0.01 hPa (20 °C) Bulk density 650 kg/m3 Solubility 1.6 g/l LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 7360 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rat > 2000 mg/kg Hazard Pictogram(s) Hazard Statement(s) H315: Causes skin irritation. H319: Causes serious eye irritation. Precautionary Statement(s) P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P280: Wear protective gloves/ eye protection/ face protection. P302 + P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water. P305 + P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P332 + P313: If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/ attention. P337 + P313: If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/ attention. Signal Word Warning Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 3 Relatively unreactive organic reagents should be collected in container A. If halogenated, they should be collected in container B. For solid residues use container C. Categories of danger irritant Storage Store at +15°C to +25°C. Assay (acidimetric, calc. on anhydrous substance) 99.0 – 101.0 % Assay (HPLC, calc. on anhydrous substance) 98.0 – 102.0 % Identity passes test Appearance of solution (5 %; ethanol 96 %) passes test Melting range (lower value) ≥ 133 °C Melting range (upper value) ≤ 135 °C Heavy metals (as Pb) ≤ 0.0010 % As (Arsenic) ≤ 0.0003 % Cd (Cadmium) ≤ 0.001 % Cu (Copper) ≤ 0.001 % Hg (Mercury) ≤ 0.0001 % Pb (Lead) ≤ 0.0002 % Zn (Zinc) ≤ 0.001 % Aldehydes (as Acetaldehyd) ≤ 0.15 % Acetone ≤ 5000 ppm Other residual solvents (ICH Q3C) excluded by the manufacturing process Thermal stability (105 °C) No coloration Loss on drying ≤ 0.5 % Water ≤ 0.5 % Sulfated ash ≤ 0.2 % Urea
CAS NO: 57-13-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA: CH4N2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 60.06
Description Synonyms Carbamide, Carbonyl diamide, Diaminomethanone, Carbonyldiamine Product Information CAS number 57-13-6 Grade ACS,Reag. Ph Eur Hill Formula CH₄N₂O Chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂ Molar Mass 60.05 g/mol HS Code 3105 10 00 Structure formula Image Quality Level MQ200 Physicochemical Information Density 1.32 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 134 °C pH value 7.5 – 9.5 (480 g/l, H₂O, 25 °C) Vapor pressure <0.1 hPa (25 °C) Bulk density 720 – 760 kg/m3 Solubility 1000 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 8471 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rat 8200 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS YR6250000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 3 Relatively unreactive organic reagents should be collected in container A. If halogenated, they should be collected in container B. For solid residues use container C. Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +15°C to +25°C. Specifications Assay (ex N) 99.0 – 100.5 % Assay (ex N, calc. on dried substance) 99.0 – 101.5 % Purity (DSC (differential scanning calorimetry)) ≥ 99.5 mol% Identity (IR-spectrum) passes test Appearance of solution (10 %; Wasser; color) colourless Appearance of solution (10 %; Wasser; clarity) clear In water insoluble matter ≤ 0.003 % Acidity, Alkalinity ≤ 0.0005 meq/g Melting point (DSC) 132 – 135 °C NH₄ (Ammonium) ≤ 0.0500 % Chloride (Cl) ≤ 0.0005 % Sulfate (SO₄) ≤ 0.001 % Heavy metals (as Pb) ≤ 0.0004 % Biuret ≤ 0.05 % Sulfated ash (600 °C) ≤ 0.005 % Cu (Copper) ≤ 0.0001 % Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.0001 % Pb (Lead) ≤ 0.0002 % Loss on Drying (105 °C) ≤ 1.0 % Corresponds to ACS, Reag. Ph Eur
Showing 25–36 of 37 items