Products
Showing 15–28 of 74 items
Calcium Gluconate
CAS NO 18016-24-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA : C12H24CaO15
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 448.39
Chemical name: Calcium Gluconate Monohydrate Similar Products: 299-28-5( Ca salt) Category: impurities,metabolites,pharmaceutical standards,intermediates,Fine Chemicals Synonyms: Calcium (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate Hydrate; Calcium bis[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate] Monohydrate;Calcium di(D-Gluconate) Monohydrate; D-Gluconic Acid Calcium Salt Monohydrate; Calcium D-Gluconate Monohydrate; Molecular form: C12H24CaO15 Appearance: NA Storage: 2-8°C Refrigerator Shipping Conditions: Ambient Applications: NA Calcium Phosphate Di Basic
CAS NO: 7757-93-9
Molecular Formula: CaHPO4
Molecular Weight: 136.06
Description Synonyms Calcium orthophosphate, Calcium phosphate dibasic Description Calcium hydrogen phosphate Product Information CAS number 7757-93-9 EC number 231-826-1 Grade Ph Eur,BP,USP,FCC,E 341 (ii) Hill Formula CaHO₄P Chemical formula CaHPO₄ Molar Mass 136.06 g/mol HS Code 2835 25 00 Quality Level MQ500 Physicochemical Information Density 2.89 g/cm3 (20 °C) Melting Point 370 °C (decomposition) pH value 7 (10 g/l, H₂O, 20 °C) suspension Bulk density 900 kg/m3 Solubility 0.1 g/l Toxicological Information LD 50 oral LD50 Rat 10000 mg/kg LD 50 dermal LD50 Rabbit > 7940 mg/kg Safety Information according to GHS RTECS TB8528000 Storage class 10 – 13 Other liquids and solids WGK WGK 1 slightly hazardous to water Disposal 14 Inorganic salts: Container I. Neutral solutions of the these salts: Container D. Before placing in Container D, check the pH with pH-Universal indicator strips Storage and Shipping Information Storage Store at +2°C to +30°C. Transport Information Declaration (railroad and road) ADR, RID Kein Gefahrgut Declaration (transport by air) IATA- DGR No Dangerous Good Declaration (transport by sea) IMDG- Code No Dangerous Good Specifications Identity passes test Assay (complexometric) 97.5 – 102.5 % Assay (complexometric; calculated on dried substance) 98.0 – 102.0 % Substances insoluble in hydrochloric acid ≤ 0.2 % Carbonate (as CO₂) passes test Chloride (Cl) ≤ 0.03 % Fluoride (F) ≤ 0.0050 % Sulfate (SO₄) ≤ 0.5 % Al (Aluminium) ≤ 0.0200 % As (Arsenic) ≤ 0.0001 % Ba (Barium) passes test Cd (Cadmium)* ≤ 0.0001 Fe (Iron) ≤ 0.0400 % Hg (Mercury) ≤ 0.0001 % Ni (Nickel)* ≤ 0.0010 Pb (Lead)* ≤ 0.0001 Sr (Strontium) ≤ 0.03 % V (Vanadium)* ≤ 0.0010 % Residual solvents (ICH Q3C) excluded by production process Loss on ignition (800 °C) 7.0 – 8.5 % Loss on drying ≤ 2.0 % Particle size (< 63 µm) about 99 % Elemental impurity specifications have been set considering ICH Q3D (Guideline for Elemental Impurities). Class 1-3 elements are not likely to be present above the ICH Q3D option 1 limit, unless specified and indicated (*). Corresponds to Ph.Eur.,BP,USP,FCC,E341 (ii) Conforms to the purity criteria on food additives, except for use as additive in infant and young child nutrition, according to the current European Commission Regulation. Calcium Saccharate
CAS NO: 5793-89-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA: C6H8O8•Ca•4H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 320.27
Chemical Name Calcium Saccharate Tetrahydrate Synonyms Calcium (2R,3S,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxyhexanedioate tetrahydrate; Calcium Saccharate CAS Number 5793-89-5 Appearance White to Off-White Solid Melting Point >185ºC (dec.) Molecular Weight 248.20 + x(18.02) Storage Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere Solubility Aqueous Acid (Sparingly, Sonicated) Stability Hygroscopic Category Building Blocks; Miscellaneous; Pharmaceutical/API Drug Impurities/Metabolites; Purity: ≥98% Applications D-saccharic acid calcium salt tetrahydrate is an inhibitor of beta-glucuronidase Citric Acid Anhydrous
CAS NO: 77-92-9
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- C6H8O7
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 192.13
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Colorless crystals or white powder, slightly hygroscopic in moist dry air. White or almost white, crystalline powder, colorless crystals or granules White Powder Solubility – Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 %). – Clarity of Solution – – The Test solution shows the same clarity as that of water. Appearance of solution (color) 20 % w/v. solution is clear and not more intensely colored than reference solution YS7,BYS7 OR GYS7. 20 % w/v solution is clear and color less or not more intensely colored than reference solution Y7, BY7 and GY7. The test solution is not more intensely colored than standard solution A,B, or C, or Water. Identification (A) Reaction
(B)) By IR Absorption
(C) Reaction
(D) Reaction
(E) Test of water
A. A 10 % w/v solution is strongly acidic. B. Reactions of citrates
A. 10 % w/v solution is strongly acidic B. Must comply with the Citric acid anhydrous CRS.
C. A red color develops
D. White precipitate is produced
E. Complies with the test of water.
A. By IR Spectrum
Arsenic NMT 1ppm. – – Bacterial end toxins – – The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement in the relevant dosage form monograph(S)in which citric acid monohydrate is used can be met. Sterility – – Meets the requirements for sterility. Barium Any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a mixture of 5 ml of solution and 5 ml of distilled water. – – Calcium NMT 200 ppm – – Heavy metals NMT 10 ppm NMT 10 ppm Iron NMT 50 ppm – – Readily carbonisable substance Any color produced is not more than intense than that of the a mixture of 1.0 ml of CCS and 9.0 ml of FCS. The solution is not more intensely colored than a mixture of 1 ml of red primary solution and 9 ml of yellow primary solution. The color of acid is not darker than that of a similar volume of matching fluid K Sulphates NMT 150 ppm NMT 150 ppm NMT 150 ppm Oxalic acid Any pink color is produced is not more instance than that produced by carrying out the test using 0.2 mg of oxalic acid dissolve in 4 ml of water. . NMT 360 ppm NMT 360 ppm Limit of Aluminium – NMT 0.2 PPM The fluorescencence of the test solution does not exceed that of the standard solution (0.2 µg/g) Residual Solvents – – Meets the requirements Organic Volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements Chlorides NMT 50 ppm – – Water by KF NMT 1.0 % NMT 1.0 % NMT 1.0 % Sulphated ash NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % (residue on ignition) Assay 99.0 % to 101.0 % 99.5 % – 100.5 % 99.5 % – 100.5 % Cupric Sulphate
CAS NO: 7758-99-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA : CuH10O9S
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 249.69
SPECIALITY FINE CHEMICALS (AR / LR / ACR /GR / IP / BP / USP / FSSAI )Dibasic Potassium Phosphate
CAS NO:7758-11-4
MOLECULAR FORMULA : K2HPO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 174.18
SPECIFICATION BP USP Description White or almost white powder or colorless crystals, very hygroscopic. White or almost white powder or colorless crystals, very hygroscopic. Solubility Very soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). – Appearance of solution Solution is clear & Colorless – Identification (A) ) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Reaction
A. Solution S (see Tests) is slightly alkaline B. Solution S gives reaction of phosphate
C. Solution S gives reaction of potassium
A. Solution S gives reaction of phosphate B. Solution S gives reaction of potassium
Reducing substances The solution remains faintly pink. – Heavy Metals – NMT 0.001 % Limit of Fluoride – NMT 0.001 % pH – 8.5-9.6 Monopotassium phosphate This ratio is not greater than 0.025. – Chlorides NMT200 ppm – Sulphates NMT 0.1 % – Arsenic NMT 2 ppm – Sodium NMT 0.1 % A solution tested on a platinum wire imparts no pronounced yellow color to a nonluminous flame. Limit of Monobasic OR tribasic salt – NMT 0.001 % Iron NMT10 ppm NMT 30 ppm Residual solvents – Meets the requirement Loss on Drying(at 125-130˚C) NMT 2.0 % NMT 1.0 % Assay (dried substance). 98.0 % to 101.0 % 98.0 % to 100.5 % Direct Blues 86
1%4%DIRECT TURQ. BLUE STD (Direct Blue 86)DIRECT TURQ. BLUE 135%. (Direct Blue 86)General Properties Dyeing
PropertiesExhaustionFairLevelingGoodFastness
PropertiesAcid3Alkaline3Hot Pressing3-4Day Light 1/16-7WashingAlteration2Stain3WaterAlteration2Stain3-4DischargeabilityNetural
Fairy Good
Alkaline-
FairFixation Temp. Exhaust Dyeing90°CSolubility30-40Salt and Alkali RequirementDepth of shade % (o.w.f.)Salt (g/l)Soda (g/l)Up to 0.5100.50.5 – 1.015-2012.0 – 4.020-251.5Above 4.025-302.0Exhaust Dyeing

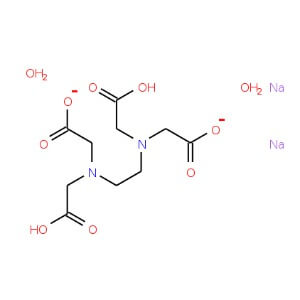
Disodium Edetate
CAS NO: 6381-92-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- C10H14N2Na2O82H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 372.24 g/ mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description A white ,crystalline powder, Odourless White or almost white, crystalline powder. White or almost white, crystalline powder. Solubility – Soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 %) – Identification A. IR
B. Reaction
C. Reaction
D. Reaction
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. No precipitate is produced.
C. No precipitate is produced.
D. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. No precipitate is produced.
C. No precipitate is produced.
D. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
A. Must comply with the disodium edetate RS
B. The red color is discharge, leaving a yellowish solution
C. It gives reaction of sodium salt.
Appearance of solution 5 % w/v solution in carbon dioxide free water is Clear & colorless Clear & colorless – pH 4.0-5.5 ( 5 % w/v solution ) 4.0-5.5 ( 5 % w/v solution ) 4.0-6.0 Loss on Drying – – 8.7 %-11.4 % Calcium – – No precipitate is formed. Impurity A Limit of nitrilotriacetic acid(USP)
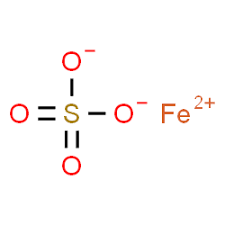
NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % Heavy metals NMT 20 ppm – NMT 50 ppm Iron NMT 80 ppm NMT 80 ppm – Assay 98.5 %-101.0 % 98.5 %-101.0 % 99.0 %-101.0 %(on Dried basis) Dried Ferrous Sulphate
CAS NO: 7720-78-7
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- FeSO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 151.91 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Grayish white to buff colored powder. Grayish white powder. Grayish white powder. Solubility – Slowly but freely soluble in water. Very soluble in boiling water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96%) – pH – 3.0-4.0 – Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Assay
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Ferrous Salt
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Irons
C. It complies with limit of assay.
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Ferrous Salt
Chloride – NMT 300 ppm – Insoluble Substances – – NMT 0.05 % Basic sulphate Producing solution that is not more than faintly turbid. – – Arsenic NMT 3 ppm – NMT 3 ppm Lead NMT 50 ppm – NMT 10 ppm Mercury – – It meets the requirements of the test for mercury Chromium – NMT 100 ppm – Copper NMT 50 ppm NMT 50 ppm – Ferric ions – NMT 0.5 % – Manganese NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % – Nickel – NMT 100 ppm – Zinc NMT 500 ppm NMT 100 ppm – Organic volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements. Residual Solvents – – Meets the requirements. Assay 86.0 % – 90.0 % 86.0 % – 90.0 % 86.0 % – 89.0 % Ferric Ammonium Citrate
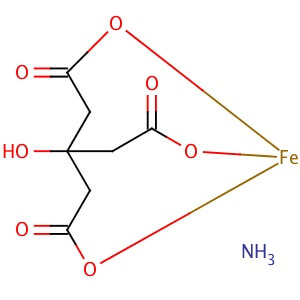
CAS NO: 1185-57-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA : C6H8O7•xFe(III)•yNH3
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
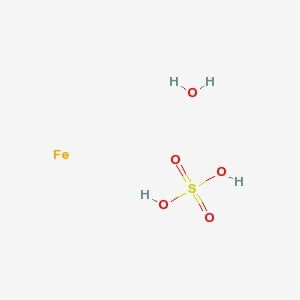
SPECIALITY FINE CHEMICALS (AR / LR / ACR /GR / IP / BP / USP / FSSAI )Ferrous Sulfate Heptahydrate
CAS NO: 7782-63-0
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- FeSO4.7H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 278.02 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Bluish green crystals or a light green, crystalline powder, odourless.Efforescent in air. On exposure To moist air, the crystals rapidly oxidize and become brown. Bluish green crystals or a light green, crystalline powder,efforescent in air. Bluish green crystals or a light green, crystalline powder, odourless.Efforescent in air. Solubility – Freely soluble in water, very soluble in boiling water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 %) Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate is oxidized in moist air, becoming brown. – pH 3.0-4.0 ( 5 % w/v Solution) 3.0-4.0 – Appearance of Solution The solution is not more opalescent than opalescent Standard. – – Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Assay
A. It gives reaction of sulfates B. It gives reaction of Ferrous Salt
A. It gives reaction of sulfates B. It gives reaction of Irons
C. It complies with limit of assay.
A. It gives reaction of sulfates B. It gives reaction of Ferrous Salt
Chloride NMT 250 ppm NMT 200 ppm – Basic sulphate Producing solution that is not more than turbid. – – Arsenic NMT 2 ppm – NMT 3 ppm Lead NMT 50 ppm – NMT 10 ppm Mercury – – It meets the requirements of the test for mercury Chromium – NMT 50 ppm – Copper NMT 50 ppm NMT 50 ppm – Ferric ions NMT 0.5 % NMT 0.3 % – Manganese NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % – Nickel – NMT 50 ppm – Zinc NMT 500 ppm NMT 50 ppm – Organic volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements. Residual Solvents – – Meets the requirements. Assay 98.0 % – 105.0 % 98.0 % – 105.0 % 99.5% -104.5 % Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate
CAS NO: 7791-18-6
MOLECULAR FORMULA: MgCl2•6H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 203.30
Application: Magnesium Chloride, Hexahydrate is a source of magnesium ion and a co-foactor for many enzymes Purity: >99% Molecular Weight: 203.3 Molecular Formula: MgCl2•6H2O Description: Magnesium Chloride, Hexahydrate is widely used as a source of magnesium ion in chemistry and molecular biology applications. In biological systems, magnesium is a co-factor for many enzymes including deoxyribonuclease (DNase) and various restriction enzymes. Also plays a role in cell membrane integrity, muscle cell physiology, cardiovascular and muscular activity, and nucleic acid structure. Magnesium chloride solution is a favorable choice as an elution buffer for antibody affinity column purifications; it is much milder on most antigens than acid elution, allowing reuse of the antigen column. Also an essential cofactor for the DNA polymerase in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (20 mg/ml), and alcohol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 116-118° C (dec.) Density : 1.57 g/cm3 at 20° C Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate
CAS NO: 10034-99-8
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- MgSO4.7H20
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 246.50 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Colorless crystals or white, Crystalline powder. White or almost white, crystalline powder or brilliant , colorless crystals. Colorless crystals or white, Crystalline powder Solubility – Freely Soluble in water , very soluble in boiling water and practically insoluble in ethanol (96 % )
Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
A : Reactions of Sulphates B : Reactions of Magnesium salts
A: It gives reaction of Sulphates. B :It gives reaction of magnesium
A: It gives reaction of Sulphates. B : It gives reaction of magnesium
pH of a 5% solution at 250C – – 5.0 – 9.2 Appearance of solution Dissolve 5 g in sufficient carbon dioxide free water to produced 50 ml (Solution A) is clear and colorless. Dissolve 5 g in sufficient carbon dioxide free water to produced 50 ml (Solution S) is clear and colorless. – Acidity or alkalinity NMT 0.2 ml of either 0.01 M hydrochloric acid or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of solution. NMT.0.2 ml of 0.01 M hydrochloric or 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of indicator. – Arsenic NMT 2 ppm.
NMT 2 ppm – Heavy metals NMT 10 ppm.
– NMT 10 ppm Selenium – NMT 30 ppm Iron NMT 200 ppm. NMT 20 ppm NMT 20 ppm Chloride NMT. 300 ppm NMT. 300 ppm
NMT. 140 ppm Organic Volatile impurities – Meets the requirement Residual Solvents – Meets the requirement Loss on drying 48.0 to 52.0 %
48.0 % – 52.0 % NMT 2.0 % Loss on Ignition – – 40.0%-52.0% Assay (on dried basis) 99.0 % to 100.5 % 99.0 % – 100.5 % 99.0%- 100.5%
Showing 15–28 of 74 items