Products
Showing 55–63 of 74 items
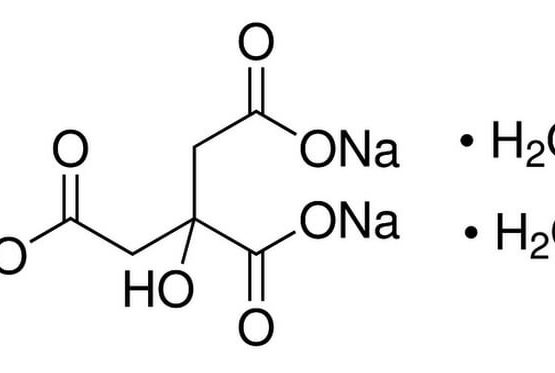
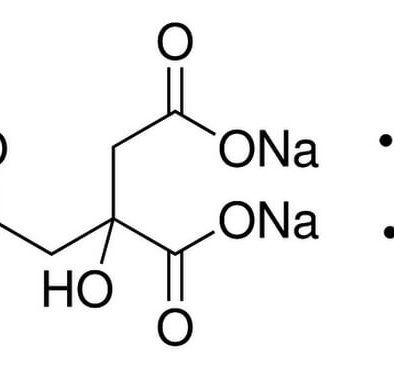
Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate
CAS NO: 6132-04-3
Molecular Formula: C6H5O7•2H2O•3Na
Molecular Weight: 294.1Alternate Names: Citric acid trisodium salt dihydrate; Trisodium citrate dihydrate Application: Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate (Molecular Biology Grade) is for the preparation of total ribosomal RNA from E. coli CAS Number 6132-04-3 Purity: ≥99.5% Molecular Weight: 294.1 Molecular Formula: C6H5O7•2H2O•3Na Description Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate (Molecular Biology Grade) is a source of Citric acid, a key metabolic intermediate. Citrate is the starting point of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Its concentration also coordinates several other metabolic pathways. Citric acid can form complexes with various cations, particularly with iron and calcium. In animals, citric acid improves the utilization of nutritional calcium. Usage : Preparation Instructions: One gram of sodium citrate dissolves in 1.3 ml of water at 25 °C and in 0.6 ml of boiling water. Poorly soluble in alcohol. pH: 7.5 – 9.0 (0.1 M in H2O, 25°C) Storage/Stability: Citrate buffers (pH 3-5) exhibit excellent stability at room temperature. Dilute solutions of citric acid (non-sterile) may ferment if left at room temperature. Non-sterile solutions should be stable for months stored at 2-8 °C. Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (29.4 g/L at 20 °C). Insoluble in alcohol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : >300° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 309.6° C at 760 mmHg Density : 1.86 g/cm3 Refractive Index : n20D ~1.58 (Predicted) pK Values : pKa: pK1: 3.14, pK2: 4.76, pK3: 6.40 Sodium Gluconate
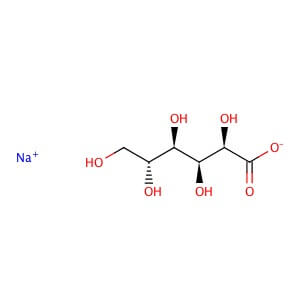
CAS NO: 527-07-1
MOLECULAR FORMULA : C6H11O7•Na
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 218.14
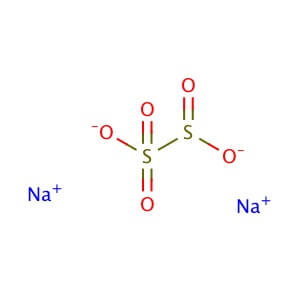
SPECIALITY FINE CHEMICALS (AR / LR / ACR /GR / IP / BP / USP / FSSAI )Sodium Metabisulphite
CAS NO: 7681-57-4
MOLECULAR FORMULA : S2O5•2Na
MOLECULAR WEIGHT : 190.1
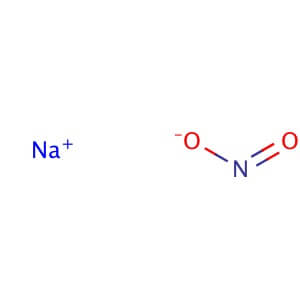
SPECIALITY FINE CHEMICALS (AR / LR / ACR /GR / IP / BP / USP / FSSAI )Sodium Nitrite
CAS NO : 7632-00-0
Molecular Formula: NaNO2
Molecular Weight: 69.00
Application: Sodium nitrite is a strong oxidizer but stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage Purity: ≥97% Supplemental Information: This is classified as a Dangerous Good for transport and may be subject to additional shipping charges. Description Sodium Nitrite is soluble in water and readily forms colorless hexagonal crystals. It is a strong oxidizer but stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. Technical Information Appearance : Crystalline or powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (820 mg/ml at 20° C), methanol (4.5 mg/ml), ethanol (3 mg/ml), ether (slightly), and NH3 (very soluble). Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 271° C (lit.) Boiling Point : 320° C Density : 2.17 g/cm3 at 20° C IC50 : HL-60: IC50 = 94 µM (human) Ki Data : Salmonella Typhimurium carbonic anhydrase : Ki= 320 µM Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Anhydrous
CAS NO : 7558-79-4
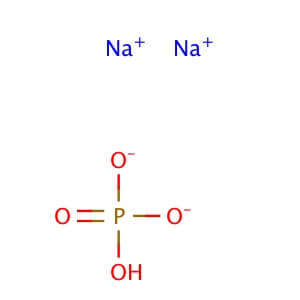
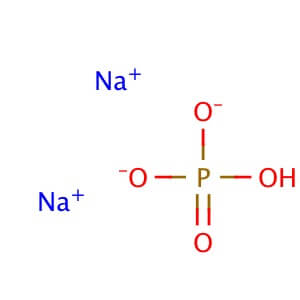
Molecular Formula:Na2HPO4
Molecular Weight: 141.96 g/mol
CAS No: 7558-79-4 MOLECULAR FORMULA: Na2HPO4 MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 141.98 Alternate Names: Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is also known as Disodium phosphate. Application: Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is reagent with high buffering capacity for molecular biology, biochemistry, and chromatography. Purity: ≥99% Description Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is a reagent with very high buffering capacity. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic is especially useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic in the preparation of biological buffers. Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic can be used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Additional forms available: Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate Sodium phosphate dibasic solution Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (118 mg/ml at 25° C). Insoluble in ethanol, alcohol, methanol, and n-octanol. Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 240.00° C Density : 1.52 g/cm3 Ki Data : CA IV: Ki= 9.8 µM (human) pK Values : pKa: pK1: 2.15 in phosphoric acid (25 C), pK2: 6.82 in phosphoric acid (25 C), pK3: 12.38 in phosphoric acid (25 C) Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dihydrate
CAS NO: 10028-24-7
Molecular Formula: Na2HPO4•2H2O
Molecular Weight: 177.99
Alternate Names: Disodium phosphate dihydrate;Disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate is a reagent with high buffering capacity Purity: ≥98% Description Sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline and crystalline granules Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Dodecahydrate
CAS NO: 10039-32-4
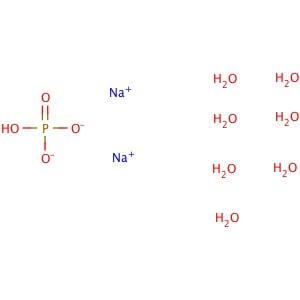
Molecular Formula: HPO4•2Na•12H2O
Molecular Weight: 358.14
Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate is a reagent with high buffering capacity CAS Number: 10039-32-4 Purity: ≥98% Molecular Weight: 358.14 Molecular Formula: HPO4•2Na•12H2O Supplemental Information: This is classified as a Dangerous Good for transport and may be subject to additional shipping charges. Description Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic (sc-202342, sc-215883 or sc-251042) in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Heptahydrate
CAS NO: 7782-85-6
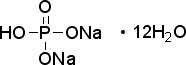
Molecular Formula:Na2HPO4•7H2O
Molecular Weight: 268.07
Application: Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate is A high buffering capacity reagent CAS Number :7782-85-6 Purity: ≥98% Molecular Weight: 268.07 Molecular Formula: Na2HPO4•7H2O Descripton Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble. Useful in conjunction with Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic (sc-202342, sc-215883 or sc-251042) in the preparation of biological buffers. Used in many applications including the purification of antibodies. Appearance : Crystalline Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (100 mg/ml). Storage : Store at room temperature Melting Point : 48° C Density : 1.68 g/cm3 at 25° C (lit.) Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Anhydrous
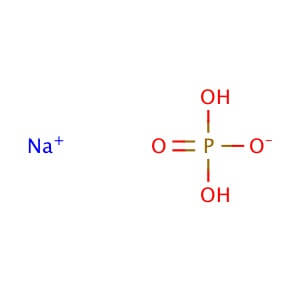
CAS NO: 7558-80-7
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- NaH2PO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 120.00 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description A white powder or colorless crystals. White, slightly deliquescent crystals or granules. White, slightly deliquescent crystals or granules. Solubility – Very soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol (96 %). – Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Reaction
(D) LOD
A: It gives reaction of phosphates.
B: It gives reaction of sodium salts.
A : 10 % solution is slightly acidic B: It gives reaction of Phosphates.
C: It gives reaction of Sodium Salts.
D : Complies with the test for loss on drying
A: It gives reaction of phosphates.
B: It gives reaction of sodium salts.
pH 4.1 – 4.5 4.2 – 4.5 4.1 – 4.5 Insoluble Substances NMT 0.2 % – NMT 0.2 % Chloride NMT 140 ppm NMT 200 ppm NMT 140 ppm Sulphate NMT 1500 ppm NMT 300 ppm NMT 1500 ppm Al , Ca & related –element Not became turbid when rendered slightly alkaline to litmus paper with 6 M ammonium hydroxide. – Not became turbid when rendered slightly alkaline to litmus paper Arsenic NMT 8 ppm NMT 2 ppm NMT 8 ppm Heavy metals NMT 20 ppm – NMT 20 ppm Water by KF NMT 2.0 % – NMT 2.0 % Organic volatile impurities – – Meets the requirement Residual Solvents – Meets the requirement Iron – NMT.10 ppm – Reducing substance – The solution retains a slight red color. – LOD ( at 1300C ) – NMT 1.0% – Assay (on dry basis) 98.0 % – 103.0 % 98.0 % – 100.5% 98.0%-103.0%
Showing 55–63 of 74 items