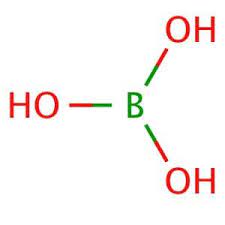
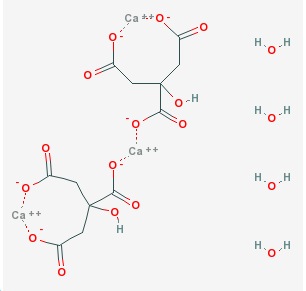
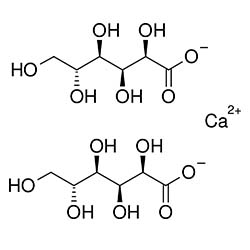
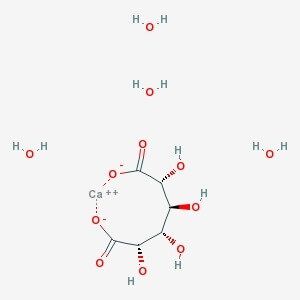
Boric Acid
CAS NO: 10043-35-3
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- H3BO3
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 61.83
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description White, Crystalline powder or colorless shiny plates, unctuous to the touch or white crystals, odorless White or almost white, crystalline powder, colorless, shiny plates greasy to the touch, or white or almost white crystals. White or almost white, crystalline powder, colorless, shiny plates greasy to the touch, or white or almost white crystals. Solubility – Soluble in water and in ethanol (96 %), freely soluble in boiling water and in glycerol ( 85 %). – Appearance of solution (10% w/v solution)
3.5 % w/v solution in boiling water is clear and colorless. 3.3 % w/v solution is clear and color less. – Identification (A) By color
(B) Reaction
A: The flame has a green border. B: 3.3 %w/v the solution is faintly acid.
A: The flame has green border. B: 3.3 % w/v solution is acidic.
It responds to the tests for borate Ph ( 3.3 % w/v solution) 3.8-4.8 3.8 – 4.8 – Solubility in ethanol (96% )
The solution is not more opalescent than opalescence standard OS2 and colorless The solution has not more opalescent than reference suspension II and colorless. – Organic matter – It does not darken on progressive heating to dull redness – Sulphates NMT 450 ppm NMT 450 ppm – Arsenic NMT 10 ppm – – Heavy metal NMT 20 ppm – NMT 20 ppm Loss on drying NMT 0.5 % – NMT 0.5 % Residual solvents Meets the requirements Assay 99.5 % to 100.5 % ( on dry basis) 99.0 % – 100.5 % 99.5 % to 100.5% (on dry basis ) Calcium Citrate
CAS NO: 5785-44-4
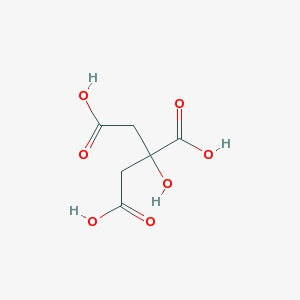
Molecular Formula: Ca3(C6H5O7)2•4H2O
Molecular Weight: 570.50
Synonyms Calcium(II) citrate, Tricalcium citrate Product Information Grade DAC,USP,E 333,FCC Hill Formula C₁₂H₁₀Ca₃O₁₄ * 4 H₂O Molar Mass 570.51 g/mol HS Code 2918 15 00 Appearance : Powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in 0.1 M HCl (0.01 M at 20° C), and water (1 g/l at 20° C). Storage : Store at room temperature Boiling Point : 309.6° C at 760 mmHg (Predicted) Calcium Gluconate
CAS NO 18016-24-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA : C12H24CaO15
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 448.39
Chemical name: Calcium Gluconate Monohydrate Similar Products: 299-28-5( Ca salt) Category: impurities,metabolites,pharmaceutical standards,intermediates,Fine Chemicals Synonyms: Calcium (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate Hydrate; Calcium bis[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate] Monohydrate;Calcium di(D-Gluconate) Monohydrate; D-Gluconic Acid Calcium Salt Monohydrate; Calcium D-Gluconate Monohydrate; Molecular form: C12H24CaO15 Appearance: NA Storage: 2-8°C Refrigerator Shipping Conditions: Ambient Applications: NA Calcium Saccharate
CAS NO: 5793-89-5
MOLECULAR FORMULA: C6H8O8•Ca•4H2O
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 320.27
Chemical Name Calcium Saccharate Tetrahydrate Synonyms Calcium (2R,3S,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxyhexanedioate tetrahydrate; Calcium Saccharate CAS Number 5793-89-5 Appearance White to Off-White Solid Melting Point >185ºC (dec.) Molecular Weight 248.20 + x(18.02) Storage Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere Solubility Aqueous Acid (Sparingly, Sonicated) Stability Hygroscopic Category Building Blocks; Miscellaneous; Pharmaceutical/API Drug Impurities/Metabolites; Purity: ≥98% Applications D-saccharic acid calcium salt tetrahydrate is an inhibitor of beta-glucuronidase Citric Acid Anhydrous
CAS NO: 77-92-9
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- C6H8O7
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 192.13
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Colorless crystals or white powder, slightly hygroscopic in moist dry air. White or almost white, crystalline powder, colorless crystals or granules White Powder Solubility – Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 %). – Clarity of Solution – – The Test solution shows the same clarity as that of water. Appearance of solution (color) 20 % w/v. solution is clear and not more intensely colored than reference solution YS7,BYS7 OR GYS7. 20 % w/v solution is clear and color less or not more intensely colored than reference solution Y7, BY7 and GY7. The test solution is not more intensely colored than standard solution A,B, or C, or Water. Identification (A) Reaction
(B)) By IR Absorption
(C) Reaction
(D) Reaction
(E) Test of water
A. A 10 % w/v solution is strongly acidic. B. Reactions of citrates
A. 10 % w/v solution is strongly acidic B. Must comply with the Citric acid anhydrous CRS.
C. A red color develops
D. White precipitate is produced
E. Complies with the test of water.
A. By IR Spectrum
Arsenic NMT 1ppm. – – Bacterial end toxins – – The level of bacterial endotoxins is such that the requirement in the relevant dosage form monograph(S)in which citric acid monohydrate is used can be met. Sterility – – Meets the requirements for sterility. Barium Any opalescence in the solution is not more intense than that in a mixture of 5 ml of solution and 5 ml of distilled water. – – Calcium NMT 200 ppm – – Heavy metals NMT 10 ppm NMT 10 ppm Iron NMT 50 ppm – – Readily carbonisable substance Any color produced is not more than intense than that of the a mixture of 1.0 ml of CCS and 9.0 ml of FCS. The solution is not more intensely colored than a mixture of 1 ml of red primary solution and 9 ml of yellow primary solution. The color of acid is not darker than that of a similar volume of matching fluid K Sulphates NMT 150 ppm NMT 150 ppm NMT 150 ppm Oxalic acid Any pink color is produced is not more instance than that produced by carrying out the test using 0.2 mg of oxalic acid dissolve in 4 ml of water. . NMT 360 ppm NMT 360 ppm Limit of Aluminium – NMT 0.2 PPM The fluorescencence of the test solution does not exceed that of the standard solution (0.2 µg/g) Residual Solvents – – Meets the requirements Organic Volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements Chlorides NMT 50 ppm – – Water by KF NMT 1.0 % NMT 1.0 % NMT 1.0 % Sulphated ash NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % (residue on ignition) Assay 99.0 % to 101.0 % 99.5 % – 100.5 % 99.5 % – 100.5 % Dried Ferrous Sulphate
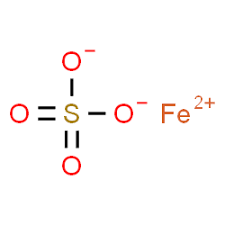
CAS NO: 7720-78-7
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- FeSO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 151.91 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description Grayish white to buff colored powder. Grayish white powder. Grayish white powder. Solubility – Slowly but freely soluble in water. Very soluble in boiling water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96%) – pH – 3.0-4.0 – Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Assay
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Ferrous Salt
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Irons
C. It complies with limit of assay.
A. Reaction of sulfates B. Reaction of Ferrous Salt
Chloride – NMT 300 ppm – Insoluble Substances – – NMT 0.05 % Basic sulphate Producing solution that is not more than faintly turbid. – – Arsenic NMT 3 ppm – NMT 3 ppm Lead NMT 50 ppm – NMT 10 ppm Mercury – – It meets the requirements of the test for mercury Chromium – NMT 100 ppm – Copper NMT 50 ppm NMT 50 ppm – Ferric ions – NMT 0.5 % – Manganese NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1 % – Nickel – NMT 100 ppm – Zinc NMT 500 ppm NMT 100 ppm – Organic volatile impurities – – Meets the requirements. Residual Solvents – – Meets the requirements. Assay 86.0 % – 90.0 % 86.0 % – 90.0 % 86.0 % – 89.0 % Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Anhydrous
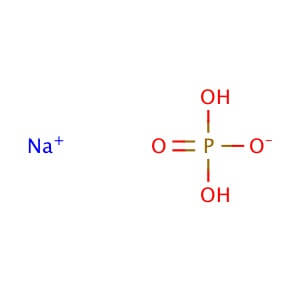
CAS NO: 7558-80-7
MOLECULAR FORMULA :- NaH2PO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :- 120.00 g/mol
SPECIFICATION IP BP USP Description A white powder or colorless crystals. White, slightly deliquescent crystals or granules. White, slightly deliquescent crystals or granules. Solubility – Very soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol (96 %). – Identification (A) Reaction
(B) Reaction
(C) Reaction
(D) LOD
A: It gives reaction of phosphates.
B: It gives reaction of sodium salts.
A : 10 % solution is slightly acidic B: It gives reaction of Phosphates.
C: It gives reaction of Sodium Salts.
D : Complies with the test for loss on drying
A: It gives reaction of phosphates.
B: It gives reaction of sodium salts.
pH 4.1 – 4.5 4.2 – 4.5 4.1 – 4.5 Insoluble Substances NMT 0.2 % – NMT 0.2 % Chloride NMT 140 ppm NMT 200 ppm NMT 140 ppm Sulphate NMT 1500 ppm NMT 300 ppm NMT 1500 ppm Al , Ca & related –element Not became turbid when rendered slightly alkaline to litmus paper with 6 M ammonium hydroxide. – Not became turbid when rendered slightly alkaline to litmus paper Arsenic NMT 8 ppm NMT 2 ppm NMT 8 ppm Heavy metals NMT 20 ppm – NMT 20 ppm Water by KF NMT 2.0 % – NMT 2.0 % Organic volatile impurities – – Meets the requirement Residual Solvents – Meets the requirement Iron – NMT.10 ppm – Reducing substance – The solution retains a slight red color. – LOD ( at 1300C ) – NMT 1.0% – Assay (on dry basis) 98.0 % – 103.0 % 98.0 % – 100.5% 98.0%-103.0% Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate
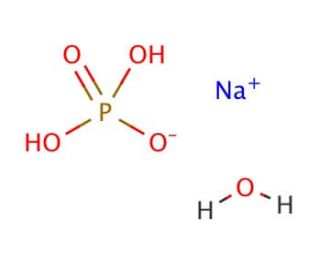
CAS NO: 10049-21-5
Synonyms: Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate; Monosodium phosphate monohydrate
Chemical Formula: H2NaO4P·H2O
Molecular Weight: 137.99 g/mol
Application: Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic, Monohydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity for formulating screens or for optimization.
CAS NO: 10049-21-5 Synonyms: Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate; Monosodium phosphate monohydrate Molecular Formula : H2NaPO4·H2O Molecular Weight: 137.99 g/mol Application: Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic, Monohydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity for formulating screens or for optimization. Purity: >99% Appearance : Crystalline powder Physical State : Solid Solubility : Soluble in water (850 mg/ml at 20 °C). pH : 4.1-4.5 Storage : Store at room temperature Density : 2.04 g/cm3 at 20° C Shelf Life : 60 Months HSN Code : 28352200 Appearance (Colour) White Appearance (Form) Crystalline powder Solubility (Turbidity) 10% aq. solution Clear Solubility (Colour) 10% aq. solution Colourless Assay (T) min. 99% pH (5% aq. solution) 4.1 – 4.5 Chloride (CI) max. 0.0005% Sulphate (SO4) max. 0.003% Iron (Fe) max. 0.001% Heavy Metals (Pb) max. 0.001% Potassium (K) max. 0.01% Absorbance (A) of 1M aq. solution in a 1cm cell v/s H2O @260nm max. 0.03 @280nm max. 0.02 Sodium Saccharine
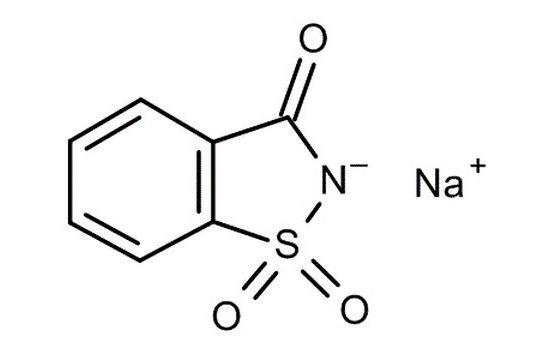
CAS No: 6155-57-3
Molecular Formula: C7H8NNaO5S
Formula Weight: 241.197 g/mol
Alternate Names: 1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-Dioxide Sodium Salt Dihydrate Technical Information Physical State : Solid Storage : Store at room temperature, 2-8°C Refrigerator Category impurities,metabolites,intermediates,pharmaceutical standards,Fine Chemicals Appearance White to Off-White Solid Applications Saccharin Sodium Salt Dihydrate is a non-nutritive sweetener; pharmaceutic aid (flavor). Saccharin was formerly listed as reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen; delisted because the cancer data are not sufficient to meet the current criteria for this listing.
Showing all 9 items